【前端必会】走进webpack生命周期,另类的学习方法
背景
webpack构建过程中的hooks都有什么呢?除了在网上看一些文章,还可以通过更直接的办法,结合官方文档快速让你进入webpack的hook世界
写一个入口文件
//index.js
const webpack = require("webpack");
const path = require("path");
const PrintHooksPlugin = require("./PrintHooksPlugin");
const config = {
context: path.resolve(__dirname),
mode: "production",
optimization: {
minimize: false,
},
entry: "./main.js",
target: ["web", "es5"],
output: {
filename: "bundle.js",
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "dist"),
},
plugins: [new PrintHooksPlugin()],
};
const compiler = webpack(config);
compiler.run((err, stats) => {
debugger;
}); //看下打印插件
//PrintHooksPlugin.js
class PrintHooksPlugin {
constructor() {}
//打印编译器Hooks
printCompilerHooks(compiler) {
//打印编译对象
compiler.hooks.thisCompilation.tap("PrintHooksPlugin", (compilation) => {
this.printCompilationHooks(compilation);
});
//遍历compiler hooks
Object.keys(compiler.hooks).forEach((hookName) => {
compiler.hooks[hookName].tap("PrintHooksPlugin", (arg) => {
console.log(`${hookName}`, hookName, arg);
});
});
}
//打印编译(构建)Hooks
printCompilationHooks(compilation) {
let compilationHooks = compilation.hooks;
//这里添加一个正则对象,判断Hook结尾的
let reg = /Hook$/;
Object.keys(compilationHooks).forEach((hookName) => {
//获取hook函数名,判断以Hook结尾,并且不是log
let name = compilationHooks[hookName].constructor.name;
if (reg.test(name) && hookName !== "log") {
compilationHooks[hookName].tap("PrintHooksPlugin", (arg) => {
console.log(`compilation ${hookName}`, arg);
});
}
});
}
//插件入口
apply(compiler) {
console.log(compiler);
console.log(compiler.hooks.thisCompilation);
this.printCompilerHooks(compiler);
}
}
module.exports = PrintHooksPlugin; //main.js
!(function () {
console.log('hello world');
})(); 结果
打印顺序就说明了生命周期的过程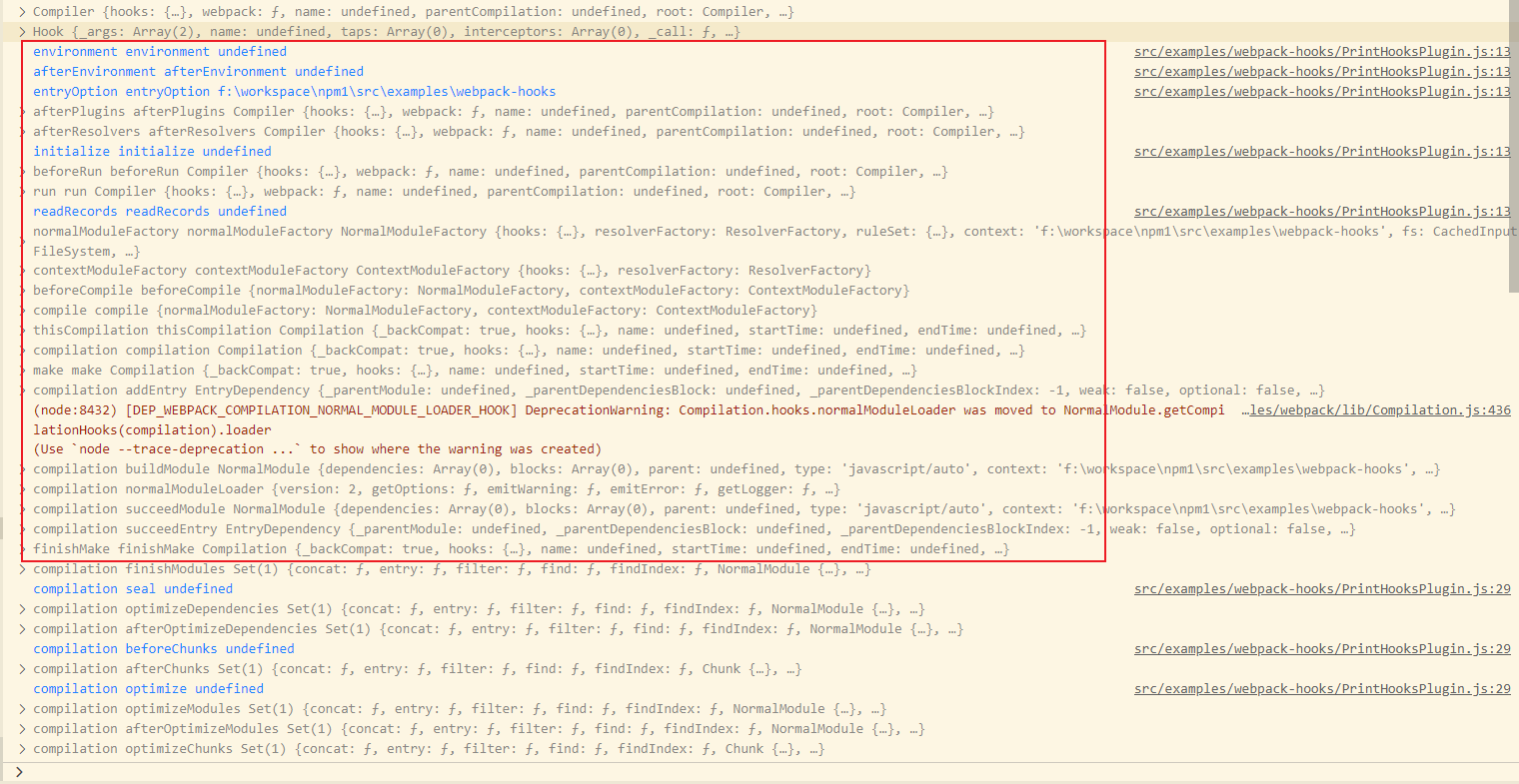
截图不全,看一下后面的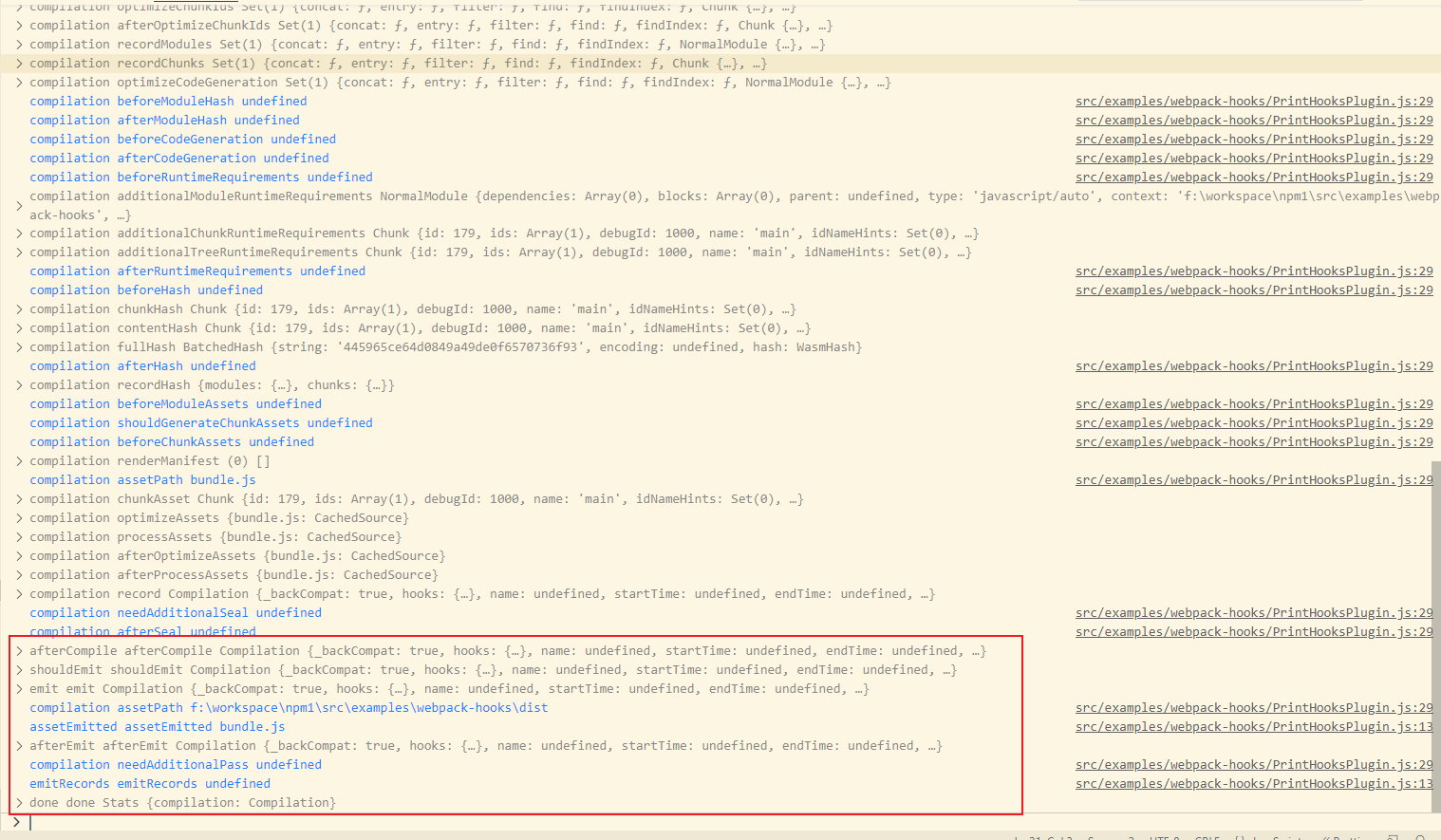
总结
- 换一种方法学习webpack的生命周期,那个hook在文档上看不太明白,直接断点,看看处理前后数据结构的变化。结合插件的源码。不信你不会
- 我们主要掌握方法,除了书本的知识,还要结合实践